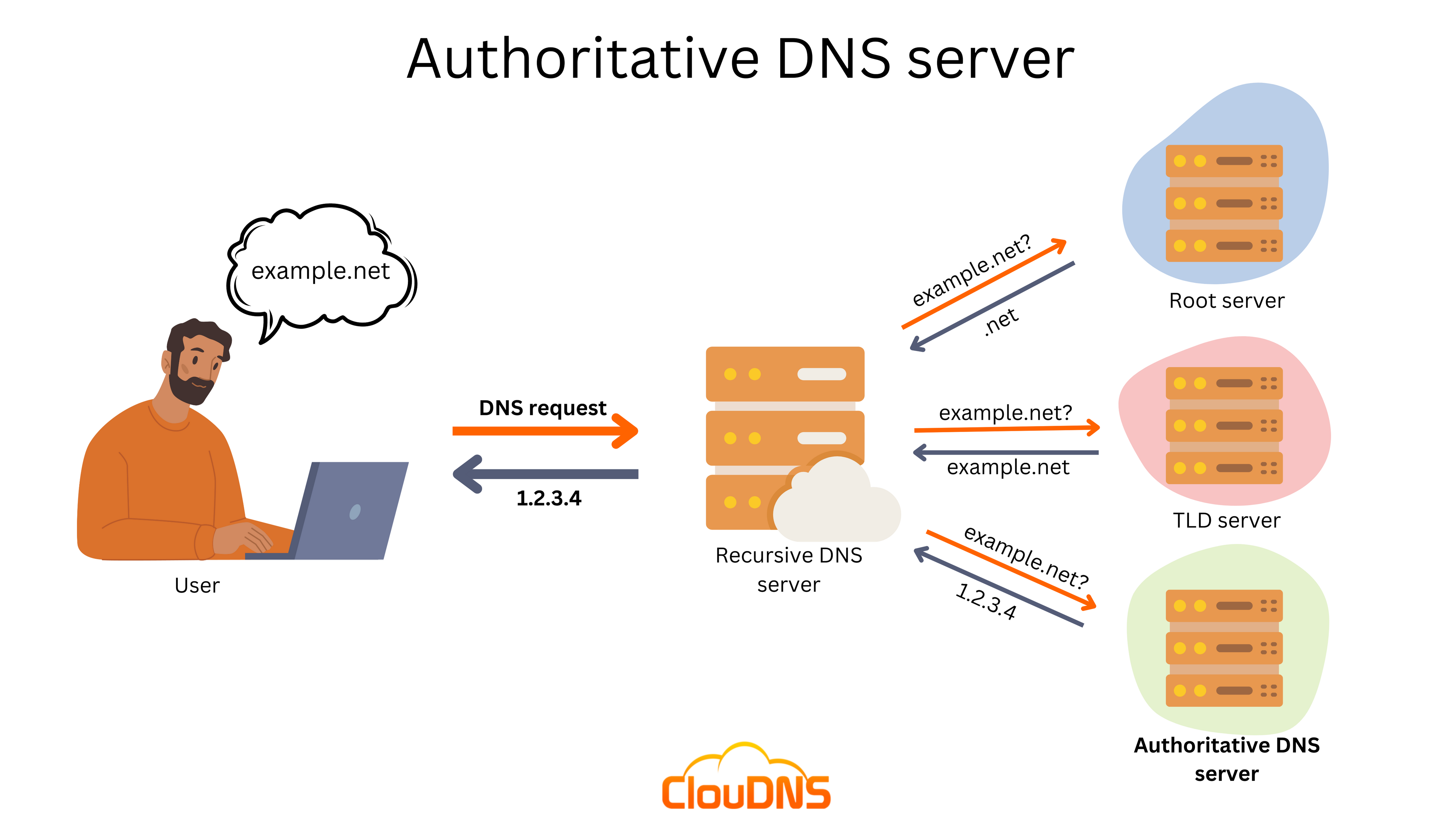
The authoritative DNS server is the final holder of the IP of the domain you are looking for. When you write a domain name in your browser, a DNS query is sent to your internet service provider (ISP). The ISP has a recursive server, which might have the needed information cached in its memory. But if the data is outdated, this recursive server needs to find the IP elsewhere. It will try to find it in other recursive servers, but if it can’t, it needs to get the IP address from an authoritative DNS server.
Table of Contents
Authoritative DNS server
Such a server is the name server, which has the original zone records. It has been configured from the original source, and it returns answers to queries that have been predetermined by the administrator.
These DNS servers are giving responses to queries just for the zones they are configured. This makes them very efficient and fast. They will not respond to recursive queries too. The requests that reach them are from Resolving name servers (resolvers) and the authoritative servers will either have the complete answer or they will pass to the name server who is responsible for it.
The authoritative servers don’t cache query results. They have data that is saved in their system.
It can be master or slave. It can store the original zone records, or a secondary server which communicates directly with the primary and copies the records directly through a DNS mechanism.
The authoritative DNS servers can be where the website is hosted or where the DNS provider is.
ClouDNS offers Authoritative DNS Servers; you can check our Managed DNS page for more information. We provide cloud-based infrastructure with 50+ points of presence and advanced features like E-mail Forwarding, Web Forwarding, Dynamic DNS, Domain parking, HTTP REST API, DNS statistics, zone sharing and more. You can even protect it from DDoS attacks.
Types of Authoritative name servers
An Authoritative server provides definitive answers to DNS queries, such as mail server IP address or web site IP address (A resource record). It does not simply return cached responses from another name server, but rather provides answers to queries about domain names that are configured in its system. We distinguish two types of Authoritative DNS servers: Primary name servers and Secondary name servers.
- A Primary name server (also known as a Master server) stores the authoritative copies of all zone records. The DNS administrator is responsible for making changes to Master server zone records. All Slave Servers receive updates via the DNS protocol’s special automatic updating mechanism and maintain an identical copy of the Master records.
- A Secondary name server (also known as a Slave server) is an exact replica of a Master server. We use it to distribute the load on the DNS server and to increase the availability of a DNS zone in the event of a failure (DNS outage, DNS attacks, etc) of the Primary server. Furthermore, it is advisable for a domain to have at least two Slave servers and one Master server.
Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!
Authoritative DNS server vs. Recursive DNS server
Both Authoritative DNS servers and Recursive DNS servers have crucial functions, and they depend on each other to fulfill their purposes. However, there are some fundamental differences between them.
Authoritative DNS servers store the most recent and accurate information (DNS records) for a domain and are able to provide the final answers for users’ DNS queries (DNS lookups). On the other hand, Recursive DNS servers only keep a copy of the DNS information for a particular amount of time, also known as Time to live (TTL). Additionally, they often have to obtain the answer for a DNS query from another server.
So let’s explain a little bit more about the differences between them!
Аuthoritative DNS server
An Аuthoritative DNS server is responsible for answering DNS queries for a particular set of DNS zones by providing information from its own data. It does not have the need to reference another source. Most commonly, it replies to the requests with one of the following types of answers:
- Authoritative DNS information (DNS records) from its own store. It could come from a master zone file, from a secondary zone duplicate transferred from a master server, from Dynamic DNS, etc.
- In case it doesn’t know the answer, it is going to direct to another nameserver. For instance, the Root name server points to the responsible TLD (Top-Level Domain) server.
- An authoritative NXDOMAIN. It replies that the requested domain name doesn’t exist.
- An authoritative empty NOERROR (NODATA) answer. The requested domain name exists, but the particular queried DNS record does not.
Recursive DNS server
The Recursive DNS server replies to DNS queries by asking other nameservers for the needed information (DNS records). In some cases, this server responds to DNS requests directly from its cache if the information is available there. In case it is not, the Recursive DNS server, also known as DNS resolver, is going to perform a search and ask the responsible authoritative servers until it finds the needed answer.
Normally, Recursive DNS servers store in their cache memory information about previously queried domain names for further use. That really reduces the network traffic and improves the performance.
Recursive DNS servers normally answer DNS queries in the following way:
- Authoritative DNS information (DNS records) from its own store, if there is any. That could be a positive response, NXDOMAIN, or NOERROR/NODATA.
- Non-authoritative DNS information that is received and cached from a previous recursive DNS query, if there is any.
- Data retrieved from remote authoritative name servers. It can be further cached and reused for answering future DNS queries.
Recursive DNS servers are most commonly used to reply to general DNS queries for users on a local network.
How to get Authoritative DNS server for a domain?
It is actually very easy to get the Authoritative DNS server for a domain name. Here we are going to show you how by using popular tools such as Dig, NSlookup, Host, and WHOIS.
- Dig command
We are going to use the Dig command and request the NS records, where NS stands for nameserver. Therefore, this DNS record is going to show us which are the authoritative DNS servers for the particular domain name or DNS zone.
Type the following:
$ dig +short NS exampledomain.com
- NSlookup command
NSlookup is another popular tool that can help you get the Authoritative DNS server for a domain name or a DNS zone. It works on Windows, Linux, and macOS. Once again, we are going to query the NS records.
Simply type the following:
$ nslookup -type=NS exampledomain.com
- Host command
Host command is a beneficial tool that you can use on your Linux or macOS device. For our purpose, to get a list of the Authoritative DNS servers, we should request the NS record.
Just write the following:
$ host -t NS exampledomain.com
- WHOIS
With the WHOIS command, you can get a list of the Authoritative DNS servers too.
Write the following:
$ whois exampledomain.com | grep -i “Name .*:”
*Make sure to replace “exampledomain.com” with the one you want to check.
Importance of Authoritative DNS Servers
Authoritative DNS servers are critical for several reasons:
- Resolution: Authoritative DNS servers translate domain names into IP addresses, enabling users to access websites and services.
- Accuracy and Reliability: They maintain up-to-date records, ensuring users receive correct IP addresses for requested domains.
- Performance: By distributing authoritative DNS servers globally, organizations can reduce latency and improve the performance of DNS resolution.
- Security: Properly configured authoritative DNS servers play a crucial role in mitigating DNS-related attacks, such as DNS spoofing and DDoS attacks.
- Domain Management: They give administrators the possibility to modify DNS records and make the needed adjustments to effectively direct traffic.
What happens if an Authoritative DNS Server goes down?
When an authoritative DNS server goes down, it can cause significant disruptions in domain resolution, leading to websites, email services, and other online applications becoming unreachable. Since authoritative DNS servers store the official DNS records for a domain, their unavailability means that recursive DNS resolvers cannot retrieve accurate IP addresses, preventing users from accessing the affected services.
Key Consequences:
- Website Inaccessibility: If all authoritative DNS servers for a domain fail, users trying to access the website will receive an error, such as NXDOMAIN.
- Email Disruptions: Mail servers rely on MX records stored in authoritative DNS servers to route emails. If these records are unavailable, email delivery may fail.
- Slower DNS Resolution: If the failed server is part of a larger network, some queries may still resolve, but with increased latency
- Business & SEO Impact: Downtime affects user experience, conversions, and search engine rankings, potentially leading to revenue loss.
How to Prevent It:
- Deploy multiple DNS servers in different geographic locations.
- Use Anycast DNS to ensure global redundancy and faster query resolution.
- Trust a reliable DNS provider with DDoS protection and uptime guarantees.
A well-configured DNS setup ensures that even if one server fails, domain resolution remains unaffected.
Best Practices
For optimal performance and security, it is best for organizations to stick with the best practices when managing authoritative DNS servers:
- Redundancy: Deploy redundant authoritative DNS servers across multiple geographic locations to improve fault tolerance and minimize downtime.
- Security Measures: Implement security measures such as DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) to protect against DNS-related threats.
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor authoritative DNS servers regularly for performance issues, unauthorized changes, and potential security breaches.
- Capacity Planning: Predict future growth and ensure that servers can handle increased DNS query loads without degradation in performance.
Common Authoritative DNS Server Misconfigurations
Even if your DNS records look right, a few common mistakes related to the configuration of your authoritative DNS server can stop your domain from working. They are the following:
Wrong nameservers at the registrar: Your domain may still be pointing to old NS records (old provider). If your domain doesn’t point to your current authoritative servers, resolvers will never reach your zone.
Missing/incorrect glue records: If your nameservers are inside your domain (for example, ns1.example.com), the parent zone may need “glue” (an A/AAAA record for the nameserver). Without it, resolvers can get stuck in a loop.
Primary/Secondary not in sync: In case you use a primary and secondary setup, the secondary servers must copy updates from the primary. Yet if zone transfers are blocked or the SOA serial number hasn’t been updated, some servers may return outdated DNS records.
Broken DNSSEC: If DNSSEC is enabled but the DS record or keys don’t match, some resolvers will reject your domain’s answers completely.
Invalid record combinations: Avoid putting a CNAME record on a name that also has other records (like A/AAAA/MX/TXT). That can cause errors or unpredictable results across resolvers.
Conclusion
So now you are familiar with what the Authoritative DNS server actually is and its crucial purpose! Its ability to provide authoritative answers to the DNS requests (DNS queries) is one of the key fundamentals of the entire DNS (Domain Name System) and the Internet as well!