A DNS zone is a fundamental part of how the Domain Name System organizes and manages data. It defines a specific portion of the DNS namespace that can be controlled and maintained independently. Whether you’re running a personal blog or managing enterprise infrastructure, understanding zones is essential for proper domain and subdomain management.
In this article, you’ll discover what they are, how they work, and the difference between Primary and Secondary zones. We’ll also guide you through the process of creating and managing them step by step. Let’s dive in and simplify this core part of DNS administration.
Table of Contents
What is a DNS zone?
DNS zone is a delegated partition of the Domain namespace, container of DNS settings and DNS records inside a DNS zone file. The DNS records point domain names to IP addresses, show information about services, serve for verification and authentication purposes and more.
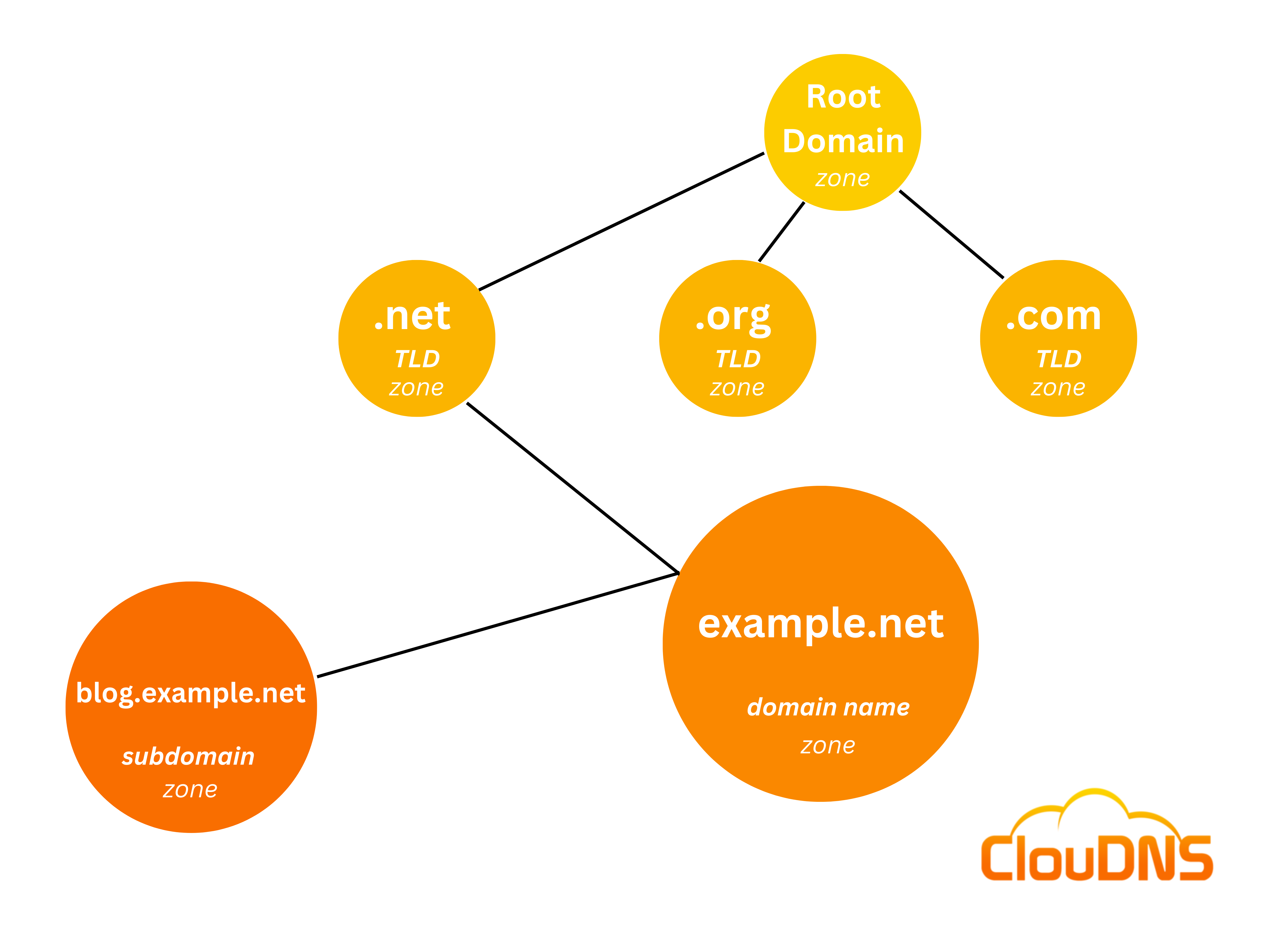
The DNS namespace can have single or multiple DNS zones, each managed by a particular DNS host/service. It has a hierarchy structure where the top is the root level, followed by the top-level domain, domain, subdomain, etc. This division helps for administrative purposes. It decentralizes the DNS, making it possible to be managed on different levels, and also reduces the tasks of nameservers by dividing their responsibilities. It is like an enormous pie. Each piece of it allows better separation of the administrative load and helps with redundancy.
There are three types of DNS zones – Primary (Master) DNS zone for control, Secondary (Slave) DNS zone for redundancy and better performance and Reverse DNS zone for network troubleshooting and for email servers IP to validation.
The first contains all the original DNS records, and the second gets them from the Primary DNS zone. The process is called DNS zone transfer. The Primary DNS server could push it, or the secondary can get the changes when its cache expires.
Don’t directly associate a DNS zone with a specific domain. A Domain Name System zone may contain single or multiple host names for the same domain; the important thing is that it is used for controlling a fraction of the namespace. DNS zones can be on the same servers too.
We also recommend that you read “What is Authoritative DNS server?“
Different types of DNS zones
There are different types of DNS zones, but in this article, we will set our eyes on just two:
- Primary (Master) DNS zone – holder of the original zone file (all the DNS records for the zone). You can manage a host through this zone.
- Secondary (Slave) DNS zone – holds a copy of the Domain Name System file. You can use them for better performance, for hiding your Primary, for backup and redundancy.
- Reverse DNS zone (rDNS) – Responsible for mapping IP addresses back to their associated domain names. This is the opposite of what a typical (forward lookup) DNS query does.
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Primary DNS zone
Primary (Master) zones contain a read/write copy of the zone data. There could be only one Master zone on one DNS server at a time. All the DNS records added manually or automatically, are written in this Primary zone of the DNS server.
The data is stored in a standard text file – .txt. The advantage is that it is easy to back it up and to recover in case of problems.
Something essential is that to be able to make changes to the Domain Name System zone, the Primary zone must be available. If the server with your Primary DNS is down, you won’t be able to make any changes.
If you want to have redundancy, you must have the zone data accessible on multiple servers.
If you want to learn how to create a Primary zone in ClouDNS, check the following step-by-step tutorial:
- Click on the sign-in button and enter your email address and your password. Once you have logged in, you will see your Dashboard. From the list, you will notice that you do not have any registered DNS zones.
- Click on the “Add new” button. In the pop-up window, click on “Master zone”. You can create your Domain Name System zone with the NS records you want. However, we recommend you to use the suggested ones.
If you want to check your domain’s NS records, we recommend you take a look at the second command from our article: 10 Most used Dig commands
- In the text field, enter your domain name without HTTP, HTTPS, or WWW. Example: yourdomain.com. Once you do it, click on the “CREATE” button.
You have successfully created your Primary (Master) zone. From the top menu, you will be able to manage your Master DNS zone with all of the available options. Here you will see all the DNS records you can create and use for your needs. From the list, you can see your hostname, the type of the record, where they are pointed to, and what the TTL is.
You can also check our wiki page about Master DNS zone.
Premium Primary DNS hosting - Try for free
Secondary DNS zone
The Secondary DNS zone is a read-only copy of the zone data. Most of the times Secondary (Slave) zones are copies of Master zones. They can also be copies of other Slave zones or Active Directory Zones.
If you try to change a DNS record on a Secondary zone, it can redirect you to another zone with read/write access. By itself, it can’t change it.
One of the primary purposes of a Slave zone is to serve as a backup. When the Primary zone is down, it can still answer requests for the zone from its copy.
Check the following step-by-step tutorial to learn how to create a Secondary (Slave) Zone in ClouDNS.
- Click on the sign-in button and enter your email address and your password.
- Once you have logged in, you will see your Dashboard. From the list, you will notice that you do not have any registered DNS.
- Click on the “Add new” button and then click on “Slave/Backup zone”
- In the first field, enter your domain name without HTTP, HTTPS, or WWW. Example: yourdomain.com. In the second field, on the right, add the IP address of your Master Server. Once you do it, click on the “Add Slave” button.
You have successfully created your Secondary (Slave) zone. From the top menu, you will see the available options for your Slave Zone. Here is also the IP address of your Primary Server.
If you want to use Secondary DNS zones, you can also review our Secondary DNS page, and decide which of our premium plans is right for you.
Now you know what a DNS zone is and the difference between these two types – Primary DNS zone and Secondary DNS zone. For any additional questions about your DNS infrastructure, you can contact our customer support.
Reverse DNS zone
A reverse DNS (rDNS) zone is a DNS zone established for the purpose of resolving IP addresses into domain names. While a standard (forward) DNS query resolves a domain name into an IP address, an rDNS or reverse DNS query does the opposite, mapping an IP address back to its associated domain name.
The Reverse DNS zone encompasses two types: Master and Slave. The Slave Reverse DNS zone acts as a safeguard, maintaining a read-only copy of the reverse DNS records while remaining in sync with the Master zone to distribute load efficiently. In contrast, the Master Reverse DNS zone is the authoritative source that houses the original mappings of IP addresses to domain names. All modifications and updates to these records are made in the Master zone. For guidance on setting up Master Reverse DNS zones, refer to the following instructions.
The utility of rDNS zones can be seen in several areas:
- Network troubleshooting: rDNS is useful for diagnosing network routing problems and pinning down the source of network attacks. By using reverse DNS lookup, network administrators can identify the hostnames associated with IP addresses appearing in log files.
- Email Verification: The SMTP protocol used for email has a step where the recipient’s mail server checks the sender’s IP address in a reverse DNS lookup. This can be used as a simple way to verify the legitimacy of the email sender and helps in spam prevention.
- For Certain Internet Services: Some Internet services, such as FTP servers, often use reverse DNS lookups as part of their control strategies.
Suggested article: FTP vs HTTP: Understanding the Key Differences
In DNS, each octet (unit) of the IP address is reversed and placed in the in-addr.arpa (for IPv4) or ip6.arpa (for IPv6) domain. For example, the IP address 192.0.2.0 is represented in a reverse DNS zone as 0.2.0.192.in-addr.arpa. The PTR (pointer) record is then used to map this to a domain.
DNS Zone VS. Domain
In the domain namespace, the biggest difference between the domains and zones is that domains provide logical structure, and the zones provide an administrative structure.
A domain is a subtree of the domain namespace. It shares its name with that of the top-most node, like yoursite.eu (eu domain). It could be divided into various zones that can be controlled separately.
A zone is a partition of the domain namespace that requires a Primary nameserver and can be managed separately. A zone can coincide with the domain and covers all of its subdomains, or it could be just a partition of the domain. You could have separate zones for mail.yoursite.com and ftp.yoursite.com for your domain yoursite.com.
DNS Zone Delegation
DNS zone delegation is the process of assigning authority over a specific portion of a domain’s namespace to a different DNS server. This is typically done by the owner of the primary domain when they want to delegate control over a subdomain to another party or server. The delegation is accomplished by adding NS (Name Server) records to the parent zone, pointing to the DNS servers that will manage the delegated subzone. This allows the parent zone to direct queries for the subdomain to the appropriate authoritative DNS servers, ensuring efficient and accurate resolution of DNS queries within the delegated zone.
For example, a large organization might manage a primary domain like example.com and have various subdomains such as hr.example.com, blog.example.com, and dev.example.com. By delegating these subdomains to different DNS servers, the organization can optimize its DNS management, ensuring faster query resolution and greater overall stability.
Security Best Practices for Managing DNS Zones
Securing your DNS zone is essential to protect your domain’s availability, integrity, and reputation. Poor security can lead to downtime, data leaks, or even domain hijacking.
Start by restricting zone transfers. Only allow trusted IP addresses (usually your Secondary DNS servers) to perform transfers. Unrestricted access can expose your entire DNS zone file to attackers.
Implement DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) to prevent spoofing and cache poisoning. DNSSEC ensures that DNS responses are authentic and haven’t been tampered with.
Use TSIG (Transaction Signature) for authenticated zone transfers. This cryptographic method helps verify that updates come from a trusted source.
Maintain strong access controls on your DNS management portal. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and limit who can edit DNS zone records.
Regularly audit your DNS records and keep backup copies of your DNS zone files. This ensures you can recover quickly in case of accidental changes.
Lastly, monitor for unusual activity, such as unauthorized record changes or abnormal traffic. Being proactive helps you detect threats early and keep your DNS zone secure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DNS zones are the building blocks of the Domain Name System, enabling efficient management of DNS records and administrative responsibilities. They play a vital role in ensuring the reliability and accessibility of online services by facilitating proper domain-to-IP address mappings.
Premium Secondary DNS hosting - Try for free