Any now and then, when we are browsing the internet, we get one of those – error 500 or error 404. What does this number mean? How many other numbers are there? In this article you will see the different categories of HTTP status codes and what do they say.
Table of Contents
What are HTTP status codes?
HTTP status codes are three-digit number that a server sends to a client in response to a request made using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It informs the client about the outcome of the request and how the server processed it. Status codes are grouped into different classes based on their meanings, such as informational, success, redirection, client error, and server error. They help in understanding whether a request was successful, encountered an error, or requires further action from the client.
HTTP status code maintenance is essential for a favorable user experience, and pivotal for SEO. To automate the process, consider using a site audit tool like SE Ranking’s solution. It will not only check HTTP status codes of all your website pages but also advise on how to better address any detected issue to improve your SEO performance.
Suggested article: FTP vs HTTP: Understanding the Key Differences
The 5 HTTP status code classifications
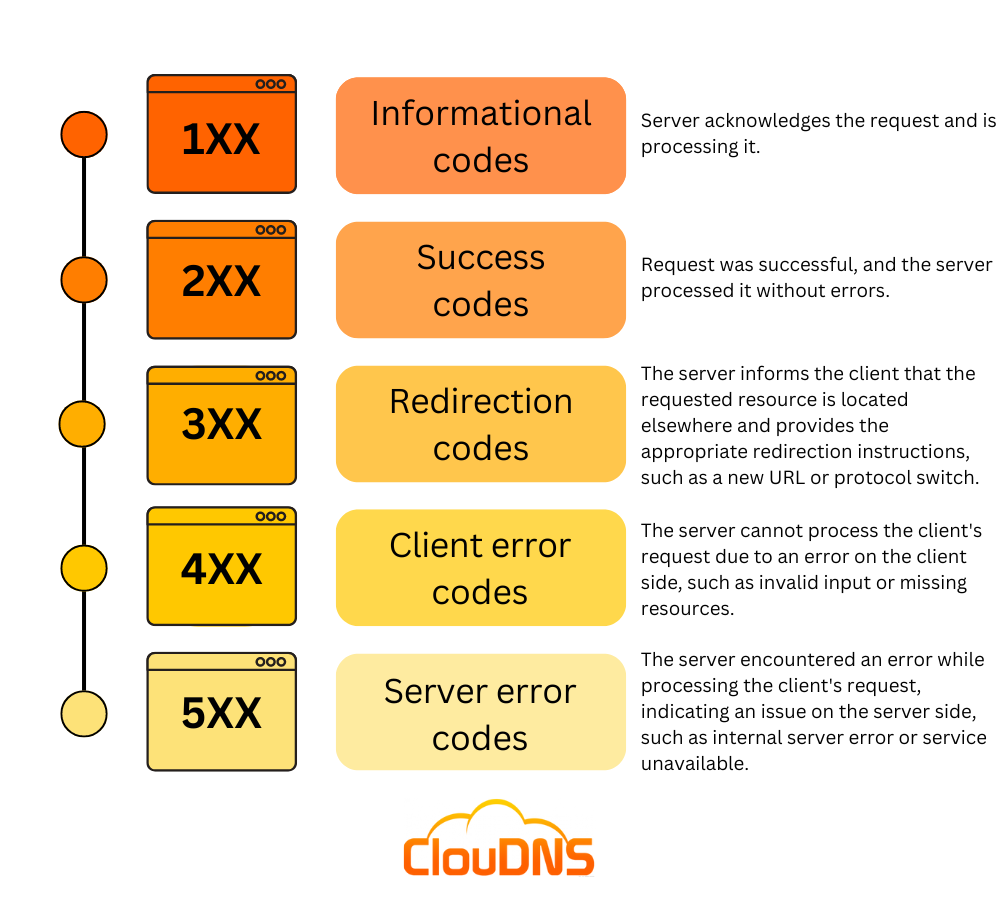
The HTTP status code is included in the response header sent by the server. Each status code carries a specific meaning, categorized into five different classes:
- Informational (1XX): These status codes indicate that the server has received the request and is continuing the process. Examples include 100 (Continue) and 101 (Switching Protocols).
- Success (2XX): These status codes indicate that the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted by the server. Examples include 200 (OK), 201 (Created), and 204 (No Content).
- Redirection (3XX): These status codes indicate that the client needs to take additional action to complete the request. It may involve redirecting the client to a different URL. Examples include 301 (Moved Permanently) and 302 (Found).
- Client Error (4XX): These status codes indicate that there was an error on the client’s side. It typically means that the request was malformed, unauthorized, or the requested resource is not available. Examples include 400 (Bad Request), 401 (Unauthorized), and 404 (Not Found).
- Server Error (5XX): These status codes indicate that there was an error on the server’s side while processing the request. It indicates that the server failed to fulfill a valid request. Examples include 500 (Internal Server Error), 502 (Bad Gateway), and 503 (Service Unavailable).
1XX Informational
The informational HTTP status codes show you that the request is received without problems, but you need to wait until it gets processed.
- 100 Continue. The server is not ready with your request. It still needs to work on it. It may be due to a large request that needs more time.
- 101 Switching Protocols. The server is changing protocols as requested by the client.
- 102 Processing. The server has received the request and is still processing it.
- 103 Early hints. The request might be too large, but you are getting some information before the final complete response.
2XX Success
Computers can show not just errors but also successes. These next codes show when a request is completed correctly.
- 200 OK. This message indicates a completed request. The request could be GET, HEAD, POST or TRACE.
- 201 Created. The request has led to the successful creation of a new resource (POST or PUT).
- 202 Accepted. The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing is not yet complete.
- 204 No content. The server, after processing properly your request, tells you that it won’t return any content.
3XX Redirection
If you have worked in SEO, you probably already know these redirects. They help you organize websites, especially after internal changes.
- 300 Multiple Choices: The requested resource has multiple choices available, and the client should select one.
- 301 Moved Permanently. If somebody moves an article from one category to another, its URL will change too. You need to point the old URL to the new one.
- 302 Found or Moved temporarily. The “moved temporary” has never been a popular and useful redirect. It was used like the 301, but if you move an item for just a short time.
What are 301 and 302 redirects and how to use them?
- 304 Not modified. Basically what this redirect tells us is that the file we requested, has no new modification from the last time we requested it. Your computer should have it in the cache.
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
4XX Client Error
In a client-server model, there are two sides, the client for easy use and server which answers queries from the different users. The 4?? errors are mostly due to a problem with the client or just answer of a request.
- 400 error, bad request. The server says that it will not continue with the request, because of an inappropriate request (probably a syntaxes error).
- 401 Unauthorized. This is when the person who wants to access has failed with the authentication.
- 403 Forbidden. Similar to 401 error, but here there is no fail, just the user has no access to that place whatsoever.
- 404 Not found. The most common error, when we are searching for an old article. 404 Not found will appear when the there is no redirect and the page is just gone.
- 405 Method Not Allowed. The method used in the request is not supported for the requested resource.
- 408 Request Timeout. The server timed out waiting for the client to send a complete request.
- 409 Conflict. The current state of the resource has a conflict that doesn’t permit the request.
5XX Server Error
Here are a few status codes that you might see often if you work with servers. This category is for the server part of the connection.
- 500 error. the most generic error possible. It doesn’t tell you anything more than the error is in the server.
- 501 Not Implemented. The server does not support or has not implemented the functionality required to fulfill the request.
- 502 error. bad gateway. The server was doing a job as a proxy or a gateway and got an invalid response from another upstream server.
- 503 Service unavailable. This you can see when the server gets too many task and overload or is down due to maintenance.
- 504 Gateway Timeout. The server, who was performing as a proxy or a gateway, didn’t receive a response in time from the upstream server. There could be a problem with the next server on the network.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported. The server does not support the HTTP protocol version used in the request.
The impact of HTTP status codes on SEO
HTTP status codes play a crucial role in SEO by influencing how search engines crawl and index your site. Here are key points:
- 200 OK: Indicates that the page is available and can be crawled and indexed by search engines.
- 301 Moved Permanently: Redirects to a new URL and transfers the SEO value (link juice) from the old URL to the new one.
- 302 Found: Indicates a temporary redirect, which does not transfer SEO value to the new URL.
- 404 Not Found: Indicates a missing page. Frequent 404 errors can harm SEO by signaling a poor user experience.
- 410 Gone: Indicates that the page has been permanently removed and should be deindexed by search engines.
- 500 Internal Server Error: Indicates a server error that prevents the page from being crawled, which can negatively affect search engine rankings.
To optimize SEO, use 301 redirects for permanent changes, fix 404 errors, avoid overusing 302 redirects, and maintain server health to prevent 500 errors. Effective management of these codes enhances search engine performance and user experience.
HTTP Status Codes vs. DNS Errors: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse HTTP status codes with DNS errors, but they refer to different issues in web communication.
- HTTP status codes indicate how a web server responds to an HTTP request made by a browser or search engine. They determine whether a page loads successfully (200 OK), is redirected (301 Moved Permanently), or encounters an error (404 Not Found, 500 Internal Server Error).
- DNS errors, on the other hand, occur when a domain name cannot be resolved to an IP address. These errors prevent the request from even reaching the web server. Examples include:
If you encounter an HTTP error, the problem is on the web server. If you see a DNS error that relates to domain resolution, the issue lies with the domain settings, DNS records, or nameservers. Checking your DNS configuration and hosting provider can help resolve DNS-related problems.
Conclusion
There are even more HTTP status codes out there, but these are the most common. Now that you know what they mean, you can understand the network better and know where to search for the problem. Hope it was interesting for you, if you want to know about another code that is not in our list, put it in the comments.