In the world of computing and networking, Telnet has been an essential tool for connecting computers and devices remotely. Despite being an old protocol, it still plays a critical role in modern-day remote access solutions. In today’s article, we will explore what Telnet is, how it works, and discuss if it’s still relevant today. So, without any further ado, let’s start!
Table of Contents
What is Telnet?
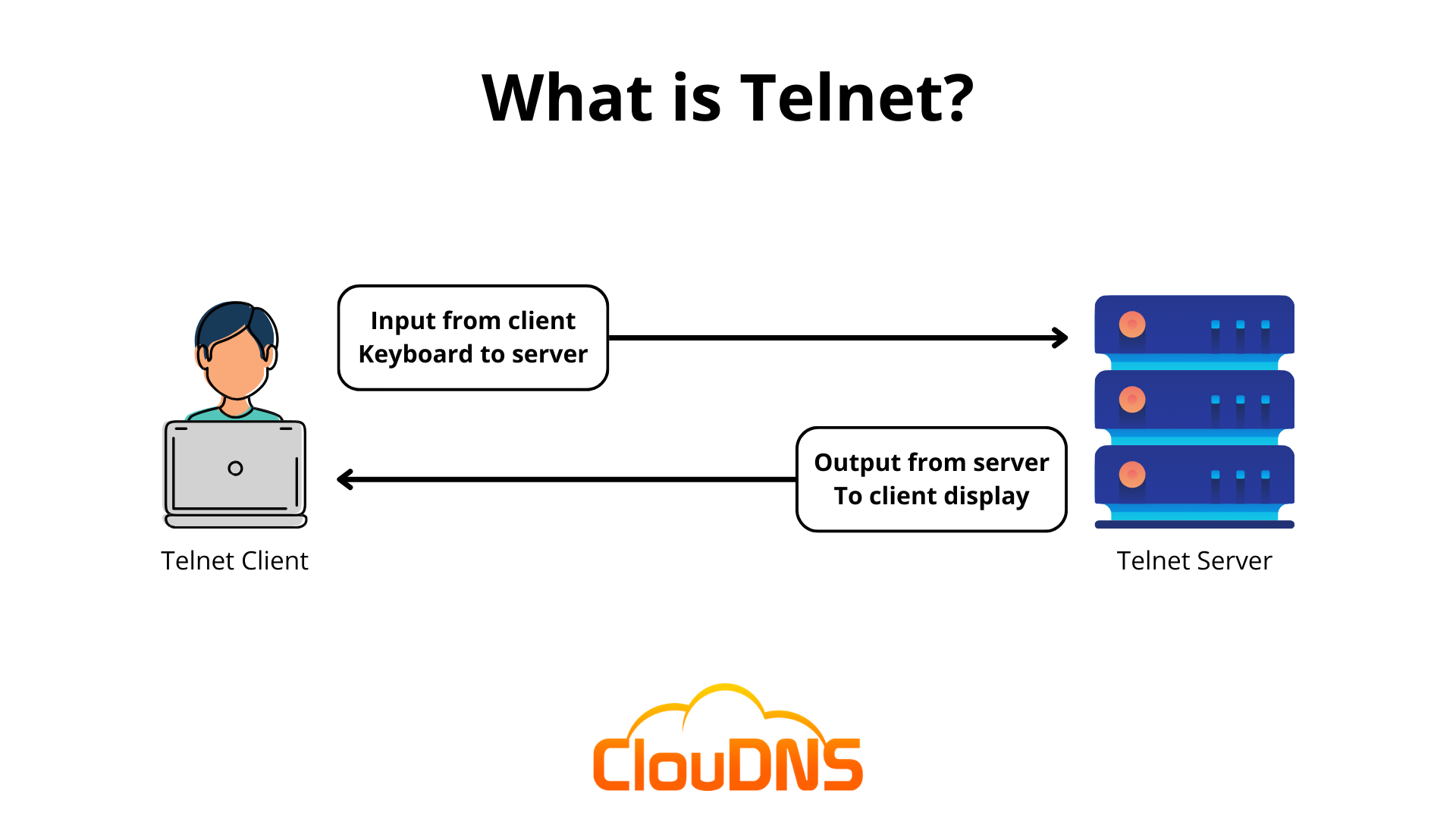
Telnet is a network protocol that allows a user to remotely access and control another computer over the Internet or local area network (LAN). It enables a user to establish a connection to a remote system and perform tasks as if they were sitting in front of that computer.
It is a client-server protocol, which means that a client device initiates the connection to a server device. The client sends commands to the server, and the server responds with output, allowing the user to interact with the remote system’s command-line interface. It uses the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) as its underlying transport protocol.
One of the key features of Telnet is that it is platform-independent, which means that it can be used to connect to a variety of different operating systems and computers. Therefore, it is a valuable tool for system administrators and developers who need to manage remote systems from different locations.
History of Telnet
The history of Telnet dates back to the early days of computer networking. It was originally developed in the late 1960s as a way to allow users of one computer to connect to another computer and use its resources remotely. The name “Telnet” comes from “TErminal NETwork,” as the protocol was designed to allow users to access remote computers using a terminal or command-line interface.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the protocol became widely used in academic and research institutions to access mainframe computers and supercomputers remotely. The protocol was also used for email and file transfer, and it became an important tool for collaboration and information sharing among researchers and academics.
Suggested page: What SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) is?
As the Internet evolved in the 1990s, Telnet became one of the standard protocols for remote access to servers and other network devices. However, its limitations in terms of security and encryption led to the development of more secure protocols like SSH (Secure Shell), which became the preferred protocol for remote access.
Despite its declining popularity in recent years, it is still used in some applications, particularly in legacy systems and applications that require remote access using a command-line interface. It definitely has an important part in the history of the Internet and the evolution of computer networking and remote access protocols.
Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!
How does it work?
Telnet allows you to connect and access a computer from a distance and control it as if you were sitting in front of it. Let’s explain the steps for using it:
Step 1: Starting a session
To start a Telnet session, you need to have a Telnet client installed on your computer. You can find Telnet clients for most operating systems (OS), including Windows, Mac, and Linux. Once you install a client, you can open it and type the command to connect to the remote computer. For example, the command looks like this: “telnet remote_computer_address”.
Step 2: Connecting to the remote computer
When you enter the command to connect to the remote computer, your Telnet client sends a request to the remote computer to establish a connection. If the remote computer accepts the connection, you’ll be prompted to enter a username and password to log in.
Step 3: Controlling the remote computer
Once you’re logged in, you can control the remote computer just as if you were sitting in front of it. You can run commands, open files, and do anything else you would normally do on the computer. The main difference is that you’re doing it remotely, so there may be a slight delay in the response time.
Step 4: Ending the session
When you’re done using it, you can end the session by typing “exit” or “quit” at the command prompt. This will disconnect you from the remote computer and return you to your own computer.
Telnet Port
Telnet primarily uses port 23 for communication, as assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). This port allows a client to establish a text-based, unencrypted connection to a remote system over the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). When a Telnet session begins, the client sends commands to the server, and the server responds, allowing the user to interact with the remote system’s command-line interface.
Although port 23 is the default, Telnet can connect to other ports as well. This is particularly useful for network troubleshooting and service testing. For example, to test an SMTP mail server on port 25, a user can type:
telnet mail.example.com 25
Despite its historical importance, port 23 is considered a major security risk because Telnet transmits all data in plaintext, including usernames and passwords. This makes it vulnerable to eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, and unauthorized access. Hackers often scan networks for open port 23 to exploit unsecured systems.
To improve security, it is recommended to disable Telnet where possible and use SSH (port 22) instead, which encrypts all communication. If Telnet is still required for legacy systems, security can be enhanced by restricting access through firewalls and VPNs to minimize risks.
Is Telnet Still Relevant Today?
Despite the rise of more advanced remote access protocols such as SSH, Telnet remains relevant today because it is simple and widely supported. Many network devices, such as routers, switches, and firewalls, still use Telnet as the primary instrument of remote management. Additionally, the protocol is useful for testing and troubleshooting network connections and services.
Common Uses of Telnet
Telnet was widely used in the early days of the Internet and still has some applications today. Here are some of the most common uses of this protocol:
- Troubleshooting network connectivity: It can be used to test connectivity to a network device or server. By establishing a Telnet connection to the device or server, you can check whether it’s reachable, identify any errors or connectivity issues, and diagnose network problems.
- Configuring network devices: Network administrators can use Telnet to remotely configure network devices like routers, switches, and firewalls. It allows them to manage the devices from a central location and make changes to the network infrastructure without physically accessing each device.
- Remote administration of servers: It can be used to remotely administer servers running a command-line interface. By establishing a Telnet session, system administrators can remotely manage and configure servers, run scripts, and perform other tasks.
- Accessing legacy systems: Some legacy computer systems still rely on Telnet for remote access. It helps connect to these systems, run applications, process data, and manage resources.
- Testing and debugging applications: The protocol can be used as a testing tool to check whether an application can connect and communicate with a remote server or device. By establishing a Telnet connection, developers and testers can verify that the application is functioning correctly and troubleshoot any issues.
Is Telnet secure?
Telnet was developed way before the mainstream adoption of the Internet. That is why it lacks modern encryption features and is not considered secure for transmitting sensitive information. It transmits data, including passwords, in plaintext, which others can easily intercept on the network. For secure communication, it is recommended to use protocols like SSH (Secure Shell), which encrypts all data transmitted between the client and server, providing both confidentiality and integrity of the data.
However, for instances where Telnet is still in use, there are some practices to enhance the security of your communications.
- VPN: If you have to use Telnet, running it over a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can secure the connection. It encrypts all traffic between your computer and the VPN exit node, which can protect your traffic from eavesdropping.
- IP Whitelisting: Restrict access to the Telnet server by allowing only specific IP addresses to connect. Note that this prevents unauthorized access but does not protect against interception of the data being transmitted.
- Telnet Over TLS/SSL: Implementing Telnet over TLS or SSL can provide encryption for Telnet sessions. This requires configuring the Telnet server to support SSL and using a Telnet client that supports SSL connections.
- Strong Authentication: Using two-factor authentication (2FA) can add an additional layer of security, but this setup might be complex and is not natively supported by standard Telnet.
- Network Monitoring and Intrusion Detection: Deploy network monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to detect and respond to suspicious activity on your network.
Telnet vs SSH: What’s the Difference and Which Should You Use?
When we talk about remote access protocols, Telnet and SSH are the two most popular and widely used choices. Although both provide a solution for remote access, they have some significant differences regarding security, functionality, and ease of use.
- Security
One of the main differences between Telnet and SSH is the level of security. Telnet transmits data in clear text, which means that anyone with access to the network can potentially intercept and read the data, including passwords and sensitive data. On the other hand, SSH encrypts data transmission, making it much more safe and secure than Telnet.
- Functionality
Another significant difference between Telnet and SSH is related to the functionality. While both protocols allow you to access a command-line interface remotely, SSH offers some additional features like file transfer, remote process management, and port forwarding. On the other hand, Telnet is more limited in terms of functionality and is mostly used for basic remote access.
- Ease of Use
Telnet is generally considered easier to use than SSH because it’s simpler and more straightforward. However, this simplicity comes at the cost of security, as Telnet lacks SSH’s encryption and authentication features. Secure Shell, while more complex, provides greater security and more advanced features, making it a better choice for enterprise environments and mission-critical applications.
SSH is typically the preferred remote access protocol due to its superior security and additional features. However, there may be some situations where Telnet is still useful, such as for legacy systems or for quick and simple remote access to a command-line interface.
Conclusion
Telnet is an old but still widely used network protocol that allows remote access and control of computers and devices. Although its popularity has declined due to the development of more secure and advanced protocols, Telnet still has its place in the world of networking and computing. It is a simple and widely supported tool that continues to have practical applications.