DMARC emerges as the solution for phishing attacks that are a real danger for every business. They can severely damage the brand name, and it can lead to less trust and leaving of clients. The attackers can spam or phish with emails that use your brand logo and look just like your emails. Even you won’t see a difference between one of these fake emails and the original emails sent from your servers. We have already talked about SPF and how it verifies the outgoing mail server. There is also another DKIM technology for signing emails. Domain-based Message Authentication (DMARC) uses both of them to take pre-defined actions. Double protection for lowering the chances of phishing and report system for better management.
Table of Contents
DMARC explained
DMARC is an authentication, policy and also reporting protocol. It uses both SPF and DKIM and adds linkage to the “From” domain name, policies for handling the incoming email in case of failure and something very important – report for the sender. That way the sender can see if there is a problem, and act on it.
The main purpose of DMARC is to protect against direct domain spoofing. If an attacker tries to send email from not authorized, DMARC will detect it and block it.
Combined with BIMI, you will also give proper protection to your brand reputation by providing authentic messages.
Why SPF and DKIM are not enough?
SPF – Sender Policy Framework has the goal to validate the senders’ servers. The receivers check the SPF record and see the IP address. It should be matching the IP address of the domain of the sender.
A problem with the SPF is that the SPF record applies to the return path of the domains, not to the domain, that shows in the “From” on the user interface. DMARC fixes this flaw with alignment, a match, between the visible “From” and the server authenticated by SPF.
DKIM – DomainKeys Identified Mail. The owner can use DKIM record to sign the emails that it sends. The emails will have extra data (encrypted) in the header that can be verified through the DNS. This technology is not flawless too. Many companies don’t rotate the key, and that can be a big problem. This is another thing, DMARC fixes. It provides rotating keys.
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
How does DMARC work?
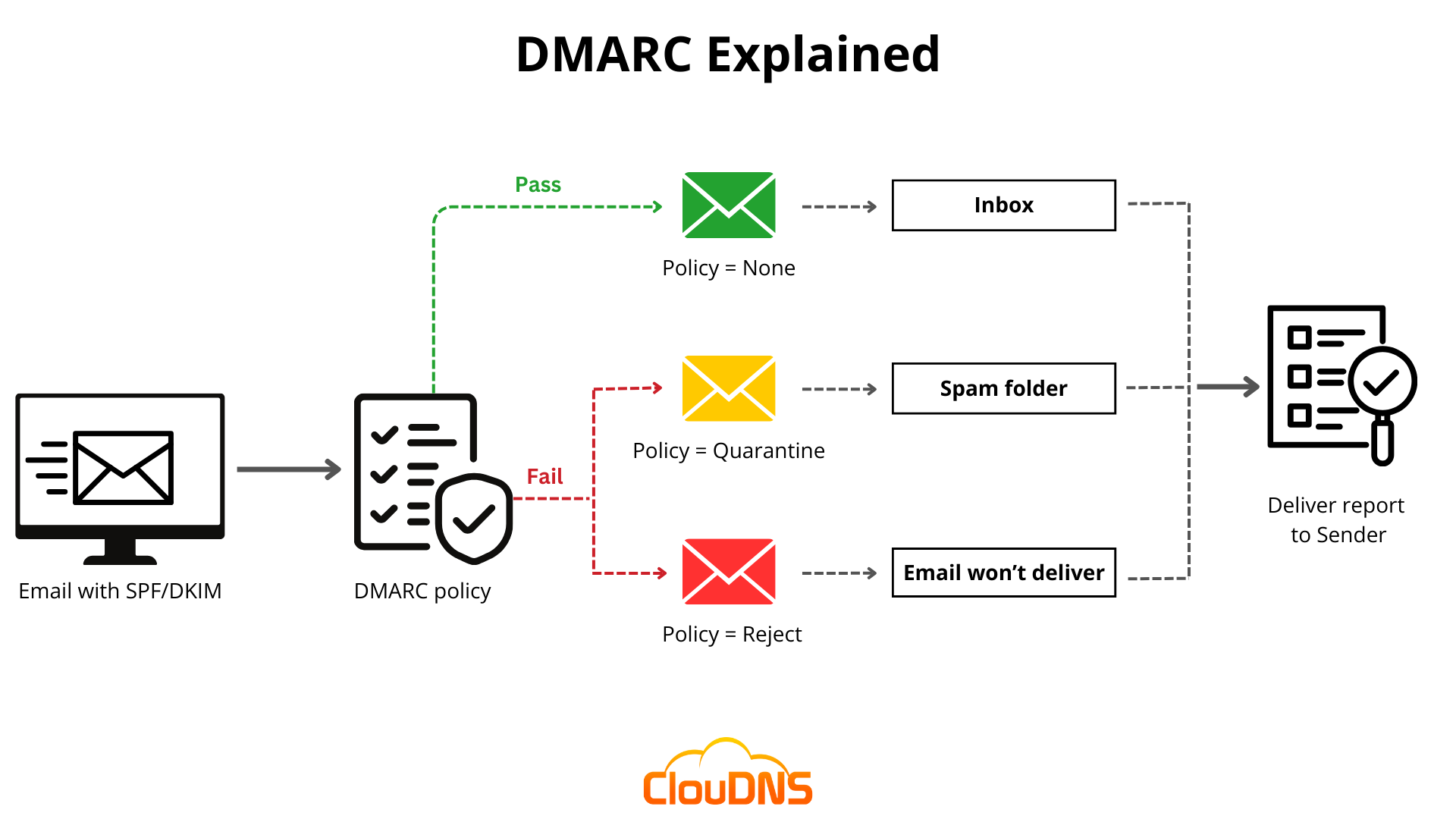
We mention already that DMARC uses policies. The administrator sets them, defining the email authentication practices and what should the receiving email server do if an email violates a policy.
When the receiving email server gets a new email, it makes a DNS lookup to check the DMARC record. It will look for:
- If the DKIM signature is valid.
- The IP address of the sender, if is one of the allowed by him (SPF record).
- If the header shows proper “domain alignment”.
With all of the above in consideration, the server DMARC policy to accept, reject or flag the email.
In the end, the server will send a message to the sender with a report.
Benefits of DMARC
Here are some of the main advantages of implementing this advanced protocol.
For the sender:
- Shows that the email uses authentication – SPF and DKIM.
- Receives a feedback about the sent email.
- Policy for failed email.
For the receiver:
- Provide authentication for the incoming emails
- Evaluating the SPF and DKIM
- See what the sender prefer – policy
- Returns feedback to the sender
DMARC Record example
DMARC records are a simple text (TXT) DNS records. They look like this:
“v=DMARC1;p=reject;pct=100;rua=mailto:postmaster@dmarcdomain.com”
- V – the version of the protocol. In the example is version 1
- Pct – % of the messages that are subject to filtering (pct=20)
- Ruf – URI for forensic reports (ruf=mailto:authfail@example.com)
- Rua – URI for aggregate reporting (rua=mailto:aggrep@example.com)
- P – Policy, organizational domain (p=quarantine)
- Sp – Policy, subdomains of the organizational domain (sp=reject)
- Adkim – Alignment for DKIM (adkim=s)
- Aspf – Alignment for SPF (aspf=r)
DMARC record generator by ClouDNS
Why use DMARC?
DMARC is a protocol used to help prevent email fraud and phishing attacks. Here’s why it’s important and why you should use it:
- Prevention of Email Spoofing: It helps prevent attackers from spoofing your domain, a common tactic in phishing attacks. By authenticating emails sent from your domain, DMARC ensures that only authorized senders can use your domain name.
- Improved Email Deliverability: Implementing it can help improve your email deliverability by reducing the chances of your legitimate emails being flagged as spam or being rejected by email servers. When email receivers see that your domain is protected by DMARC, they are more likely to deliver your emails to the inbox.
- Protection of Brand Reputation: Phishing attacks that use your domain can harm your organization’s reputation and trustworthiness. DMARC helps protect your brand reputation by preventing unauthorized use of your domain in phishing emails, thereby maintaining trust with your customers and partners.
- Visibility and Control: DMARC provides visibility into email traffic sent from your domain through reporting mechanisms. You can monitor email authentication results and receive reports on email activity, including information about legitimate and fraudulent email senders. This allows you to take proactive measures to protect your domain and email infrastructure.
How to Create and Publish a DMARC Record with ClouDNS
To create a DMARC record, you can use the ClouDNS DMARC Record Generator, which allows you to define your domain, choose a policy (None, Quarantine, or Reject), and add report email addresses for both aggregate and forensic reports. You can also set the reporting interval and protocol version, typically DMARC1.
Once the tool generates your DMARC record, publish it by adding it as a TXT record in your DNS:
- Log in to your ClouDNS account (or your DNS provider).
- Open your domain’s DNS zone.
- Add a TXT record.
- Set the hostname to _dmarc (just that, not the full domain).
- Paste the generated DMARC value into the value field.
- Save the changes.
Conclusion
DMARC can significantly lower the number of fraud emails and spam. It is not 100% bulletproof, but it adds a lot of extra protection in comparison with the other two solutions – SPF and DKIM. The reporting functionality is welcome plus too.