Welcome to the world of IPsec! In today’s digital age, protecting sensitive information from cybercriminals is crucial. That’s where IPsec comes into play. In this article, we’ll dive into what it is, how it works, and its different protocols and modes. So, without any further ado, let’s start!
Table of Contents
What is IPsec?
IPsec is a set of protocols to secure internet communication at the network layer. It was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to provide a secure way to exchange data over the Internet, ensuring that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access, interception, or modification.
IPsec is the short acronym for Internet Protocol Security. The “IP” stands for Internet Protocol, which is the main routing protocol used on the Internet for sending data to its destination using IP addresses. The “sec” stands for secure, as it provides encryption and authentication to the data transmission process, making it more secure.
Its main goal is to encrypt data, provide authentication and access control, and ensure the integrity of the data being transferred. It helps many organizations protect their data from malicious actors and ensure secure communication between devices. It is widely used for securing Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), providing a safe connection for remote access. IPsec also controls access, ensuring only authorized users can access the data or network. Additionally, it provides authentication, ensuring the data comes from a legitimate source. IPsec is a vital tool for organizations to protect their data and ensure secure communication.
Tracing its roots and evolution
The inception of IPsec can be traced back to the early 1990s, a time when the Internet was rapidly expanding, and the need for secure communication was becoming increasingly evident. Developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), IPsec was designed to secure and encrypt data at the IP layer. Over the years, IPsec has evolved, adapting to the changing landscape of digital security.
In its early stages, IPsec primarily focused on securing communication between networks. However, as the Internet grew and new threats emerged, IPsec adapted to provide more robust and versatile security solutions. Key developments included the introduction of new encryption algorithms and improved key management protocols, enhancing its ability to safeguard data against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. This evolution has established IPsec as a standard for secure Internet communication, trusted by organizations worldwide for its reliability and robustness.
Experience Industry-Leading DNS Speed with ClouDNS!
Ready for ultra-fast DNS service? Click to register and see the difference!
What is IPsec used for?
It is commonly used to establish secure connections between networks, remote users, or individual devices over the Internet. IPsec works by encrypting and authenticating the data transmitted over a network, providing confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. This ensures that sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal data are protected from unauthorized access, interception, or modification. IPsec is widely used in virtual private networks (VPNs), which allow remote workers to securely access a company’s internal network from outside the office. It is also used in secure email, voice-over-IP (VoIP), and other internet-based applications that require safe communication. Overall, IPsec is an essential tool for ensuring the privacy and security of internet communications.
How does IPsec work?
To establish a secure connection, IPsec follows a set of several steps, which are the following:
- Key exchange: Keys are essential to enable encryption. A key is a sequence of random characters used to encrypt (lock) and decrypt (unlock) messages. IPsec sets up keys with a key exchange between the connected devices. That way, every device is able to decrypt the other device’s messages.
- Packet headers and trailers: When data is transmitted over a network, it is divided into smaller units known as packets. These packets include two main components: the payload, which is the actual data being transmitted, and the headers, which provide information about the data to allow the receiving computers to process it correctly. In the context of IPsec, additional headers are added to each packet to incorporate authentication and encryption information. Moreover, it also attaches trailers to the end of each packet’s payload rather than at the beginning.
- Authentication: IPsec provides authentication for every packet. This mechanism guarantees that the packets originate from a reliable source rather than a malicious attacker.
- Encryption: It provides encryption both for the payloads and the IP headers of each packet. This ensures that data transmitted over IPsec is protected and kept confidential.
- Transmission: The encrypted IPsec packets travel across different networks to reach their target destination using the UDP transport protocol. That is a significant difference compared to regular IP traffic, which typically uses TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), which sets dedicated connections between devices. On the other hand, UDP doesn’t set such connections, which allows IPsec packets to get through firewalls.
- Decryption: At the end of the communication, the packets are decrypted, allowing applications such as web browsers to access and utilize the data.
IPsec protocols
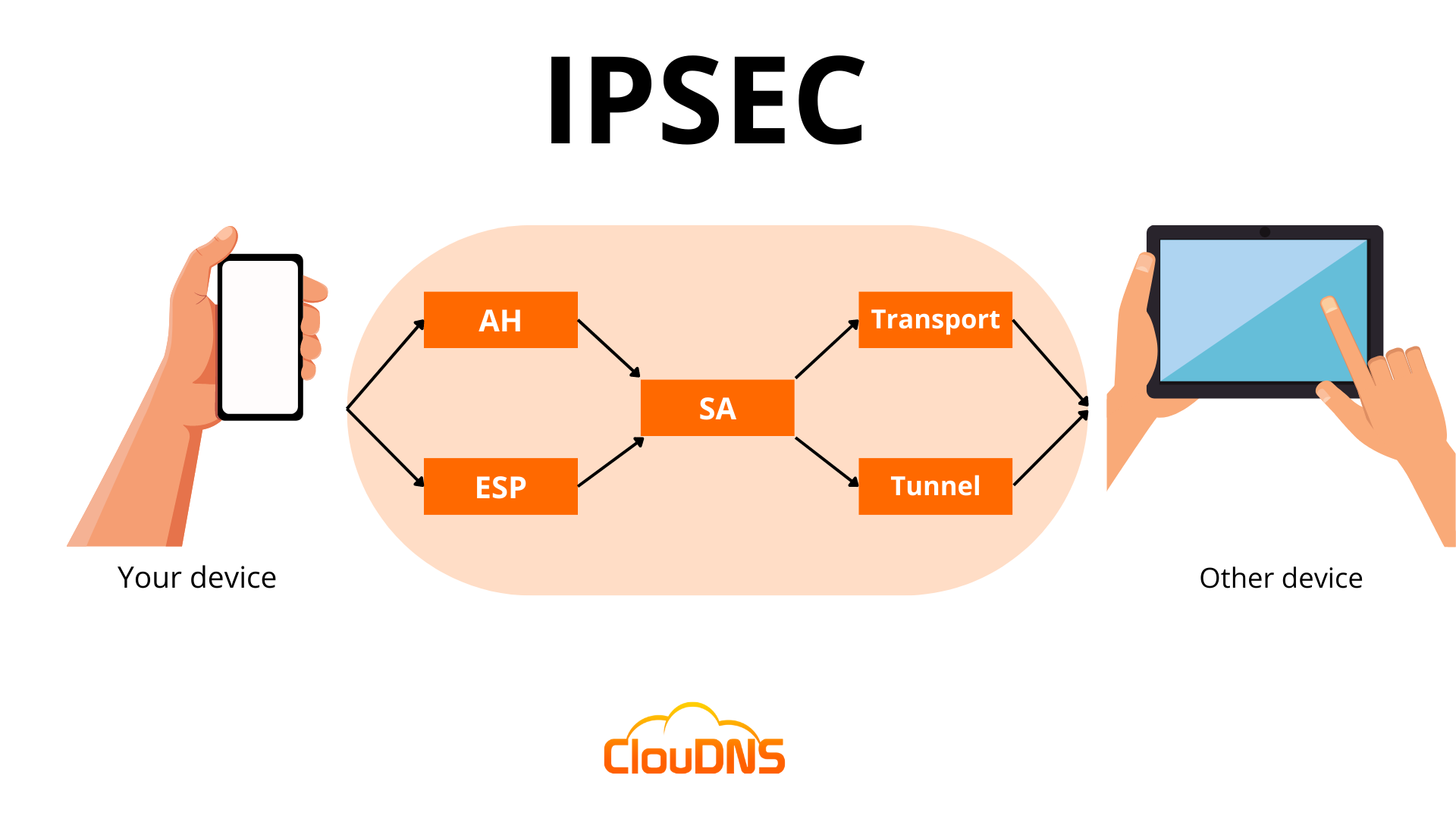
IPsec uses a variety of protocols to establish secure connections and protect data during transmission. IPsec is not one protocol but a suite of protocols. The suite includes the following:
- Authentication Header (AH): It provides data integrity and authentication and ensures that the transmitted data has not been modified or tampered with. Yet, it does not encrypt data.
- Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP): It encrypts both the IP header and the payload of each packet unless transport mode is used, in which case only the payload is encrypted. In addition, ESP adds its own header and a trailer to each data packet.
- Security Association (SA): An SA is a set of security parameters defining how two devices communicate securely. It includes information such as the encryption algorithm, authentication method, and key size. One of the most commonly used SA protocols is the Internet Key Exchange (IKE).
IPsec Modes
IPsec offers two distinct modes that provide different amounts of protection for network communication.
- Tunnel Mode: In this mode, all data, including the header and payload, is encrypted, and a new header is added. It is ideal for secure data transfer over public networks, as it provides enhanced protection against unauthorized access.
- Transport Mode: It encrypts only the payload while the IP header remains unchanged. The unencrypted header allows routers to identify the destination address of each packet, making it suitable for use in a trusted and closed network.
What is IPsec Encryption?
IPsec encryption is a process that ensures the confidentiality of data transmitted over a network by converting it into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered by authorized parties. It employs robust encryption algorithms, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES), to protect sensitive information from interception or unauthorized access.
The encryption process works by transforming plaintext data into ciphertext using encryption keys, ensuring that even if the data is intercepted, it cannot be understood without the correct decryption key. IPsec encryption can secure both the payload (data) and the headers of IP packets, depending on the mode used (Transport or Tunnel). This encryption mechanism is a cornerstone of IPsec’s functionality, enabling secure communication over public or private networks, such as in Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) or between networked devices.
Benefits
IPsec offers a number of benefits, including the following:
- Data Encryption
With IPsec, all the data transmitted over the Internet is encrypted, making it impossible for cybercriminals to intercept and read it. The privacy of the data is especially important for businesses dealing with sensitive information, such as financial or personal details.
- Authentication
It provides authentication, ensuring the communication between two endpoints is legitimate. That way, it prevents unauthorized access to the network and protects the network from various cyber-attacks. IPsec uses authentication methods to verify the identity of the users and devices on the network.
- Integrity
With IPsec, the data transmitted over the Internet is not tampered with or modified in any way. As a result, it ensures that the data received at the other end is the same as the transmitted data and that there has been no unauthorized alteration or modification.
- Compatibility
IPsec is a widely used protocol and is supported by many devices and operating systems. That signifies that businesses can use it to secure their networks without having to worry about compatibility issues.
Which port does IPsec use?
IPsec uses port 500 for its IKE (Internet Key Exchange) protocol. This port is used for the initial negotiation between two systems and to establish a secure connection. Once the connection is established, IPsec will then use a variety of other ports to send and receive data. These ports are usually randomly chosen and can range from port 4500 to port 5500.
It also uses port 4500, which allows IPsec traffic to pass through a NAT (Network Address Translation) device. This is important for allowing IPsec traffic to pass through firewalls and other security devices.
What is IPsec VPN?
An IPsec VPN is a network architecture that employs the Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) protocol suite to establish secure and encrypted communication channels over potentially unsecured networks such as the internet. This technology is designed to protect data integrity, ensure confidentiality, and authenticate data sources.
Technically, an IPsec VPN functions by encapsulating data packets and encrypting the payload with robust encryption algorithms. This process transforms the data into unreadable formats for anyone intercepting the packets. It employs two primary modes: Tunnel mode and Transport mode.
Furthermore, IPsec VPN uses sophisticated key exchange mechanisms, like IKE (Internet Key Exchange), to securely establish cryptographic keys between communicating parties. With its comprehensive approach to security, an IPsec VPN is essential for enterprises and individuals who require secure communication over the internet, especially for sensitive data transmission.
IPsec VPN vs SSL VPN
IPsec VPN and SSL VPN are both popular technologies used to secure remote access to private networks, but they operate in distinct ways and offer different benefits.
IPsec VPN
IPsec VPN establishes a secure, encrypted tunnel between two endpoints, typically between a client device and a VPN gateway or between two networks. It operates at the network layer (Layer 3), ensuring that all traffic between devices is encrypted, including non-web traffic like VoIP or file sharing. IPsec VPNs often require client-side software or hardware and are ideal for site-to-site connections and situations where security is paramount. However, IPsec can be more complex to set up and maintain.
SSL VPN
SSL VPN, on the other hand, uses the SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols to secure data transmission. It operates at the application layer (Layer 7), typically through a standard web browser, and doesn’t require special client software. SSL VPNs are often used for remote access to specific applications or web-based services. They are easier to deploy and more user-friendly, making them a great choice for individual users or organizations that need access to internal web apps.
Key Differences:
- Security: IPsec VPN provides stronger, network-wide security due to its encryption of all traffic at the network layer.
- Ease of Use: SSL VPN is more user-friendly, requiring only a browser, which makes it convenient for remote workers accessing web-based applications.
- Deployment: IPsec VPN requires more infrastructure and configuration, whereas SSL VPN is simpler to deploy for remote access solutions.
While both IPsec and SSL VPNs provide secure connections, your choice between them depends on your organization’s specific needs, such as the type of traffic, user access requirements, and deployment complexity.
Conclusion
IPsec is the superhero of internet security! It’s an essential tool for businesses dealing with sensitive information and offers benefits like authentication, integrity, and data encryption. Implementing IPsec helps keep your internet communication safe and secure!